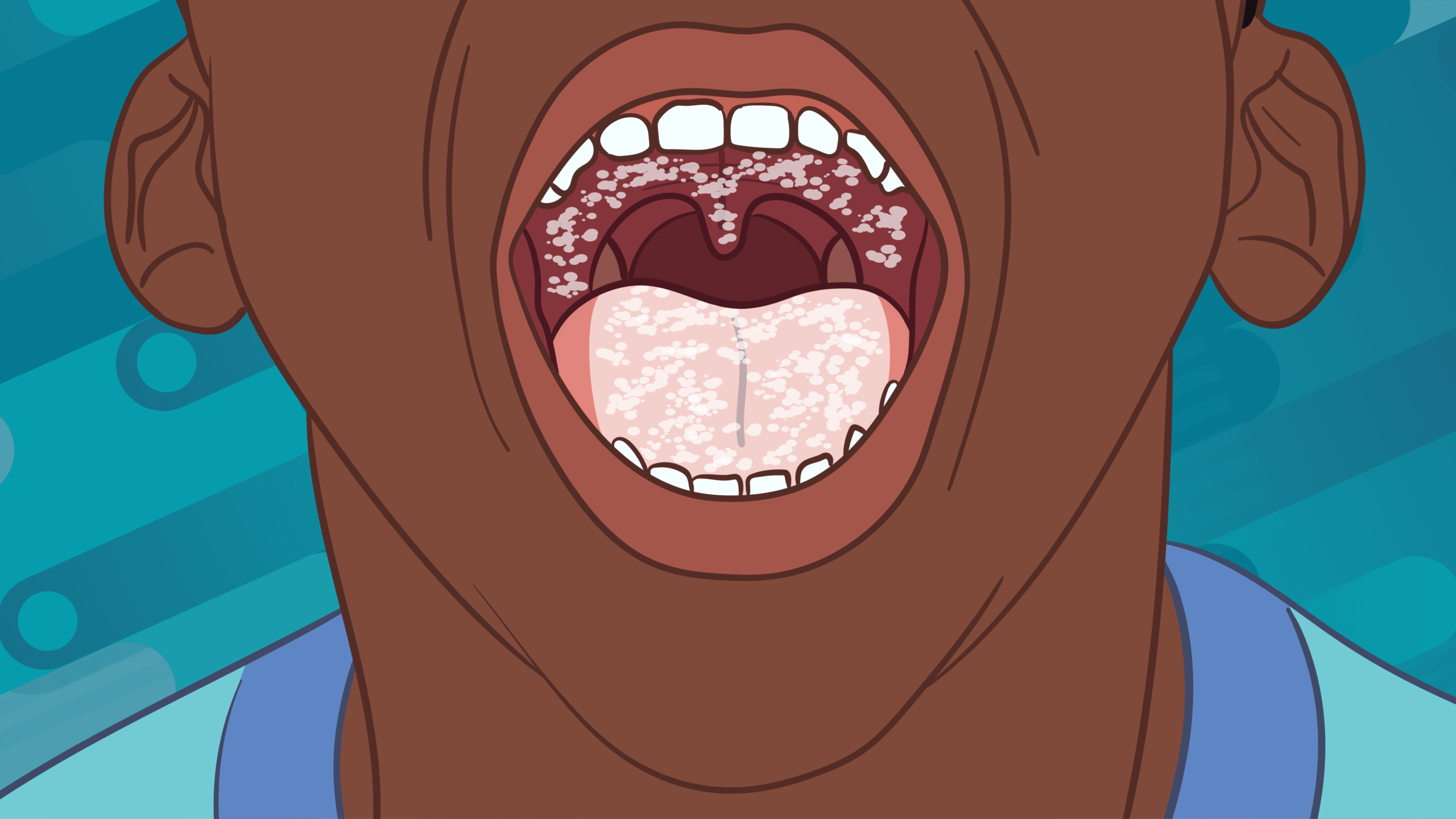
What is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis, also called a yeast infection, is caused by a fungus called Candida. It usually affects the mouth, skin, or private areas. People with weak immunity, diabetes, pregnancy, or who use long-term antibiotics are more likely to get it.
If you think you have a yeast infection, you can book a consultation with Hope Plus to speak directly with a healthcare provider who can guide you on treatment.
Causes
- A fungus called Candida albicans spreads through direct contact.
Symptoms
Candidiasis can look different depending on the area affected:
- Mouth: white patches, pain, or difficulty swallowing (oral thrush)
- Skin: redness and itching between skin folds (like under breasts or armpits)
- Private areas: itching, unusual discharge, or irritation in women (not sexually transmitted)
- Fingernails: redness or swelling around the nails (chronic paronychia)
- Stomach or food pipe: pain when swallowing, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
How it is diagnosed
Doctors usually check symptoms and may take a sample if needed:
- For vaginal infections: a swab from the vagina
- Lab tests to confirm the fungus and see which medicine works best
How it is treated
Mouth infections (thrush)
- Medicines like Nystatin to chew or swallow 4 times a day for 10 days
- Children get a smaller dose in liquid form
Private area infections
- Creams or pessaries (medicine inserted into the vagina) like Clotrimazole or Nystatin
- Severe or recurring infections may need Fluconazole tablets
Skin infections
- Keep the area dry and clean
- Use antifungal creams like Clotrimazole
- For severe cases, tablets may be needed
Nail infections
- Keep hands dry and wear gloves for wet work
- Apply steroid creams for inflammation
- Tablets may be used if creams do not help
Prevention
- Keep skin and private areas clean and dry
- Treat infections early
- Avoid taking antibiotics unnecessarily
- Practice good hygiene